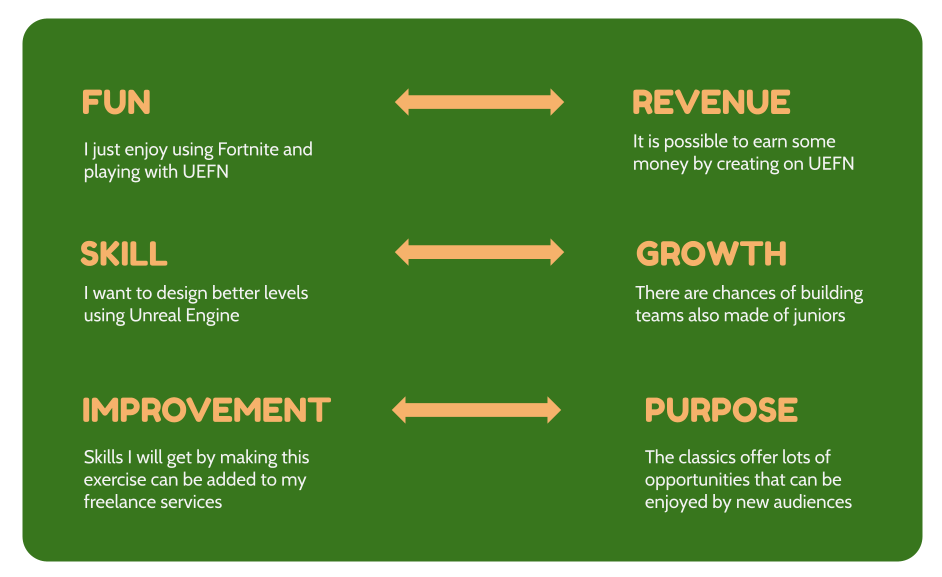
Mobile phones are nowadays in everyone’s hands. Kids are playing mostly from mobile devices (tablets are a big player, they are used also in many schools). Still, when I listen to people talking about the future of mobile games, the discussion is always going around two things:
- effective way of stealing ideas (playbooks)
- how to hack the marketing machine and get people to install your game more cheaply (performance marketing).
Well, this can be a tactic for the short term, sure. But for the long one, we need to look at things with a critical perspective: mobile games are always the freaking same. We don’t see nowadays the kind of innovation we saw when Supercell, Rovio, and King arrived on the scene. We are still repeating (and improving) formulas, that’s all. And it’s very boring. The most interesting novelties are coming from UGC experiences inside of Roblox, from one side. From the other, we see an exasperation of FOMO, dark patterns, and grinding for the addicts. We are not going too far like this.
We need more game design, more research, and more risk betting on something novel. Of course, the discourse around distribution is very important, but we are distributing always the same and listening to people who are not building interesting games. That’s a huge problem for our industry.
Generative AI will never improve profit margins for companies, AI design and art are just scams. We need to return to the basics, at the drawing board, thinking really in finding interesting formulas for people looking for fun.