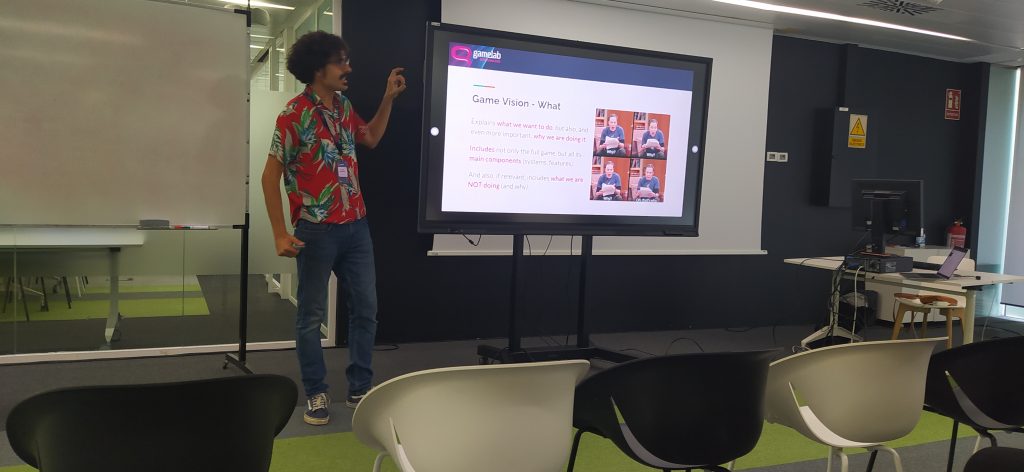
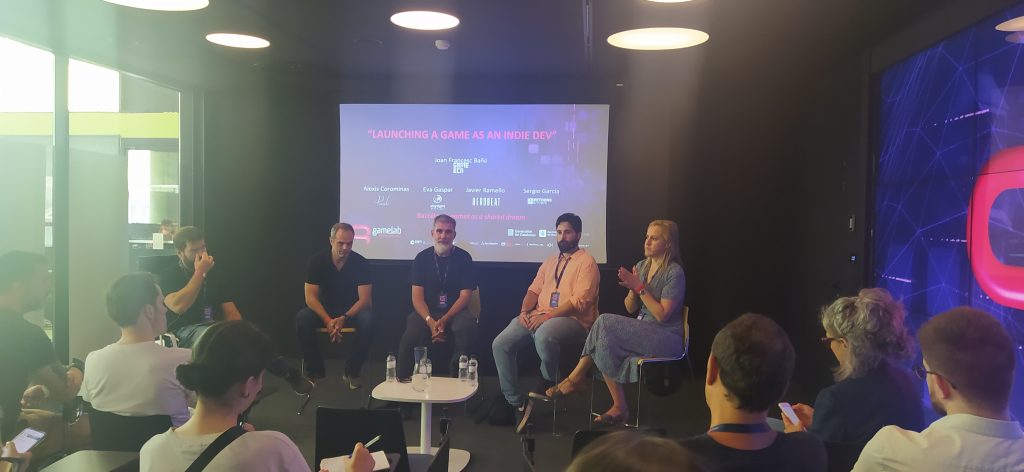
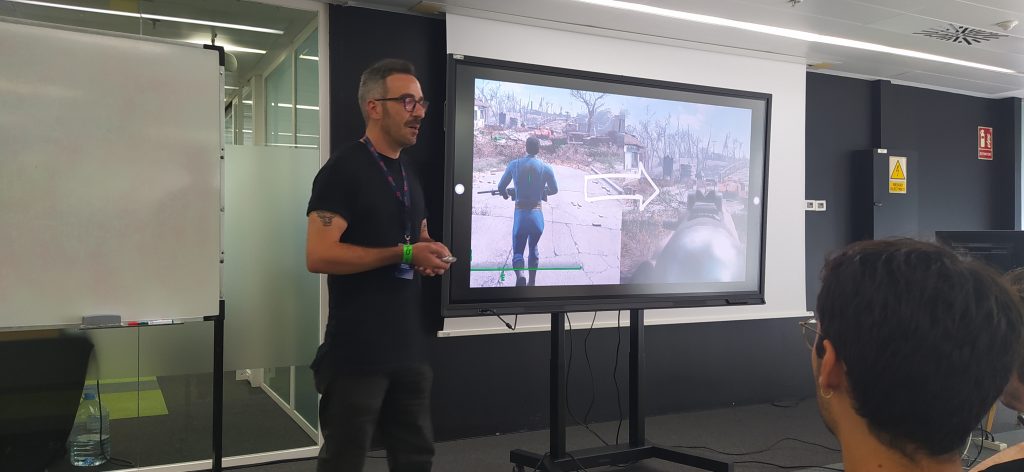
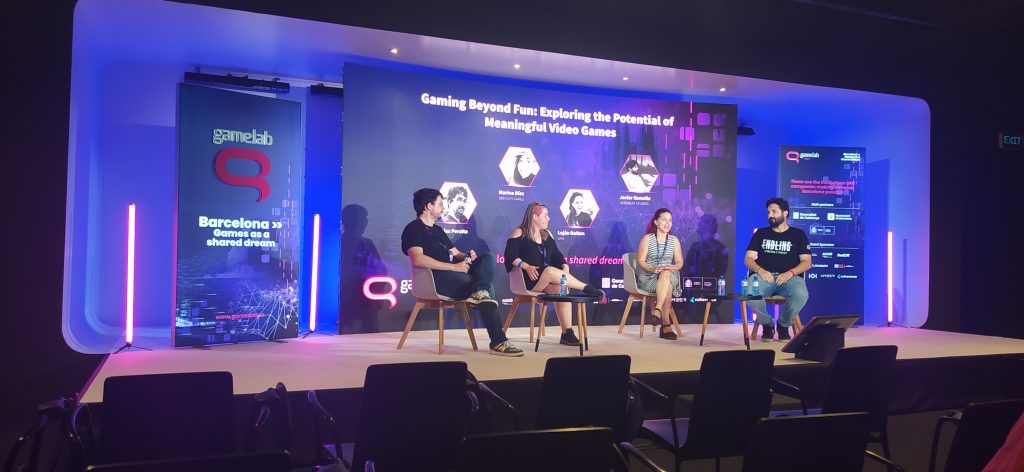
For the second day of the Gamelab I have carefully chosen two types of conferences. On one hand exponents of the indie world, and on the other people who work in the f2p mobile sector.

I did it with a very specific purpose. I have long been convinced that the two tribes, however distant, have much to learn from each other. This conviction probably made me observe specific elements. In turn, these elements have strengthened it.
The mountain
[This metaphor came to mind thanks to a story a Capoeira master told me years ago about martial arts in general.]
Let’s imagine that we want to reach a mountain’s top. In the case of video games, imagine that at this peak are the most spectacular games in history. Super Mario, but also Candy Crush Saga. There is Clash of Clans and there is Minecraft. Stardew Valley and The Legend of Zelda.
We want to get there.
There are many ways to do this. First, why do we want to do this? What drives us?
Meaning and ambition
In most indie realities there is something internal that moves people. Some experience that you want to explore, some specific fantasy they have from childhood. Emotions, memories. We can talk about meaning, in their case.

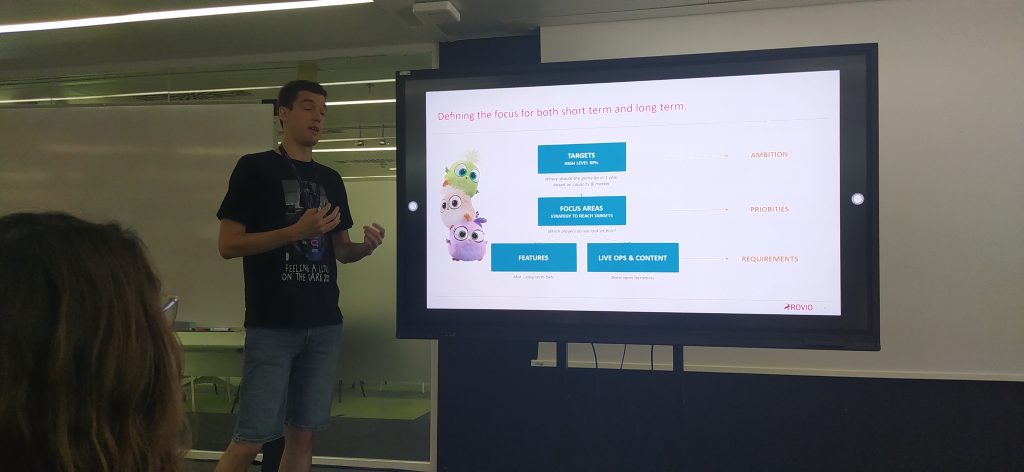
When I listen to people in the free-to-play world, there is something external. The possibility of reaching millions of people. To create a business that can grow significantly. Structuring a growth and upgrade plan that you can track using technologies and data. We can talk about ambition, in their case.
Indie companies create their games and find that there is a real market. What they are looking for is financial stability, to continue developing their games. They start with meaning, but when the results arrive, they also discover ambition.
Free-to-play companies most often start with a business opportunity. They discover that the trend is to make puzzle-casual games and look for ways to develop them. When they have years working, they understand that their ambition must be backed up with real meaning. There are millions of players out there looking for
- relaxation
- stress-relief
- connection with other people
In this exact order.

Why are they looking for it? What are the fantasies that lead these people to choose to be loyal to a specific game? What does move you to serve those people, really? The main challenge of all free-to-play actors is to make new games. New ideas. From the initial ambition, one begins to search for meaning.
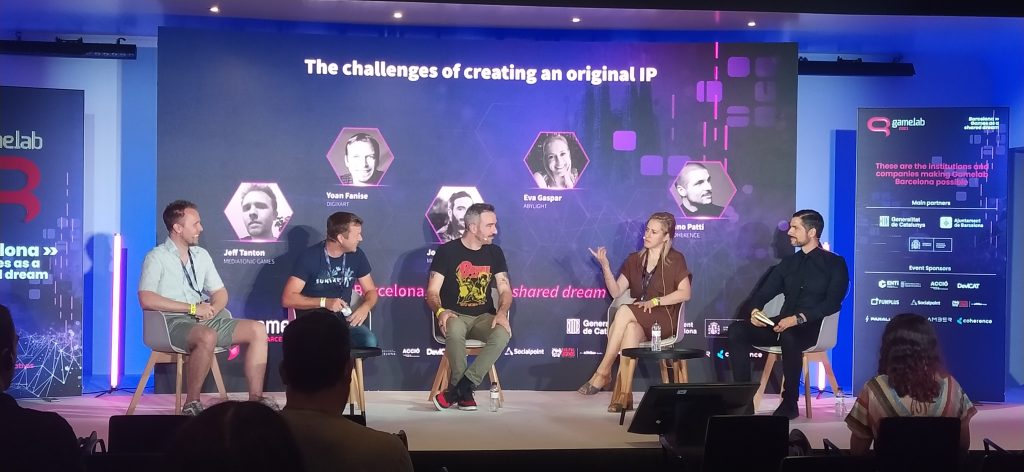
Indies and F2P can learn from each other
Indies can learn from free-to-play that a noble cause has a lot of risks that can be tackled with a data-informed approach. And I’m not talking about retention, monetization, and all these things that you hear.

I’m talking about concrete UX strategies. For me, it’s not enough to give your game to people, observe them and get feedback as I hear yesterday over and over. It is good, but not enough. You need to create concrete heuristics and turn your assumptions into numbers. Create gyms for your game. Prepare Wizard of Oz tests, and measure the behaviors of your players. Test the symbology and game icons, to understand how people interpret them.
[If you look at the paths of the mountain ahead of you, higher up you will see realities that have made it because they have overcome certain risks. Do you want to reach them? Don’t focus on your desire to walk, look at the obstacles.]

Free-to-play companies must understand that all successful products come from a strong foundation. Games offer a set of fantasies that connect with people. People keep playing these games because they find concrete meaning. This meaning translates into value, and value is what ultimately makes the business grow. If you start by exploring your competitors and seeing their numbers to choose who to follow, you go the other way. Look for the meaning first, for the fantasies that connect with people. Indie gaming has a lot to teach in that sense.
[At the base of the mountain I mentioned earlier, there are people starting paths. If other people are higher now it is because someone has already created a path. But if you want to start directly from higher up, well you have to jump. And jumping you risk rolling down.]